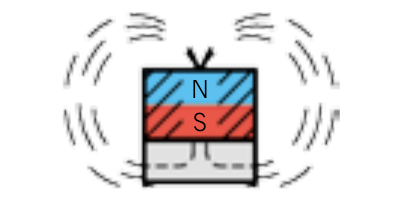
You already know that magnets are strong. The saying "opposites attract" is undoubtedly derived from the power of magnets. As you know, the north and south poles of a magnet attract each other. With a "normal" magnet, the magnetic fields move through free space.

A disc magnet in free space
When you hold two magnets close to each other, these fields pull toward one another, causing the two magnets to stick together.
Disc magnet on an iron contact surface.
How do pot magnets work? Magnetic fields do not only exist in the space around us; they also move through materials such as nickel or iron. In a pot magnet, all magnetic field lines are directed downward toward the contact surface. This concentrates the forces, increasing the strength of the pull. As a result, pot magnets are even more powerful than regular magnets.
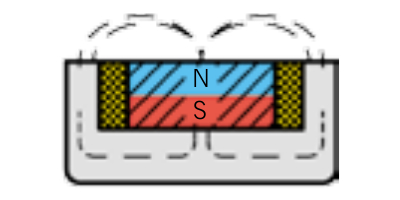
Pot magnet in free space
However, when you place two pot magnets side by side, they do not attract each other. Additionally, pot magnets are best suited for use in the home or office. They are less suitable for outdoor use because they are prone to rusting. That said, we do offer stainless steel pot magnets in our shop. These have undergone a special treatment to make them rust-proof.
There are several types of pot magnets. We have listed a few below:
- Ferrite pot magnets The most commonly used pot magnets, featuring ferrite magnetic material.
- Samarium Cobalt pot magnets Strong pot magnets that can be used at high temperatures of up to 350°C.
- Alnico pot magnets These are the least powerful and most affordable pot magnets. They can be used in temperatures up to 400°C!
- Neodymium pot magnets The strongest pot magnets available, featuring very high pull forces.
- Stainless steel pot magnets These pot magnets have a stainless steel housing. While this slightly reduces the pull force, the magnet becomes corrosion-resistant and can be used outdoors or even underwater.